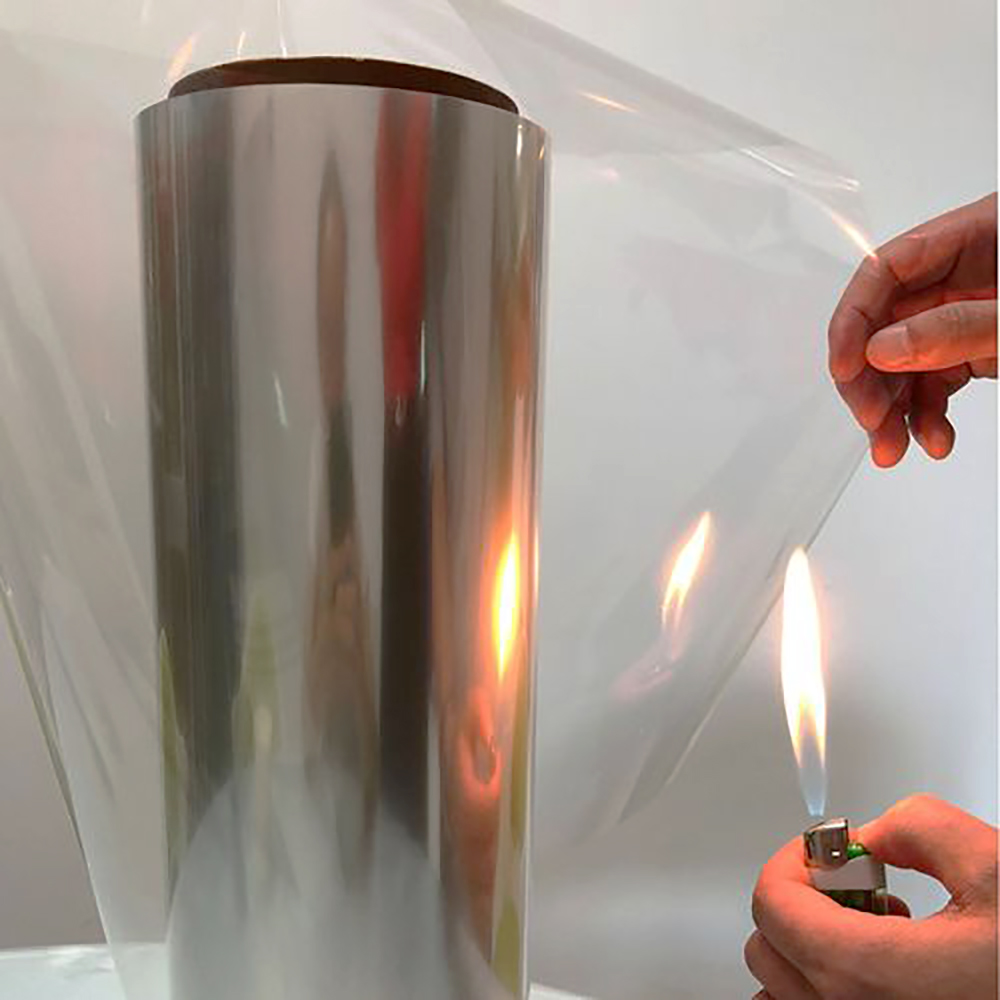
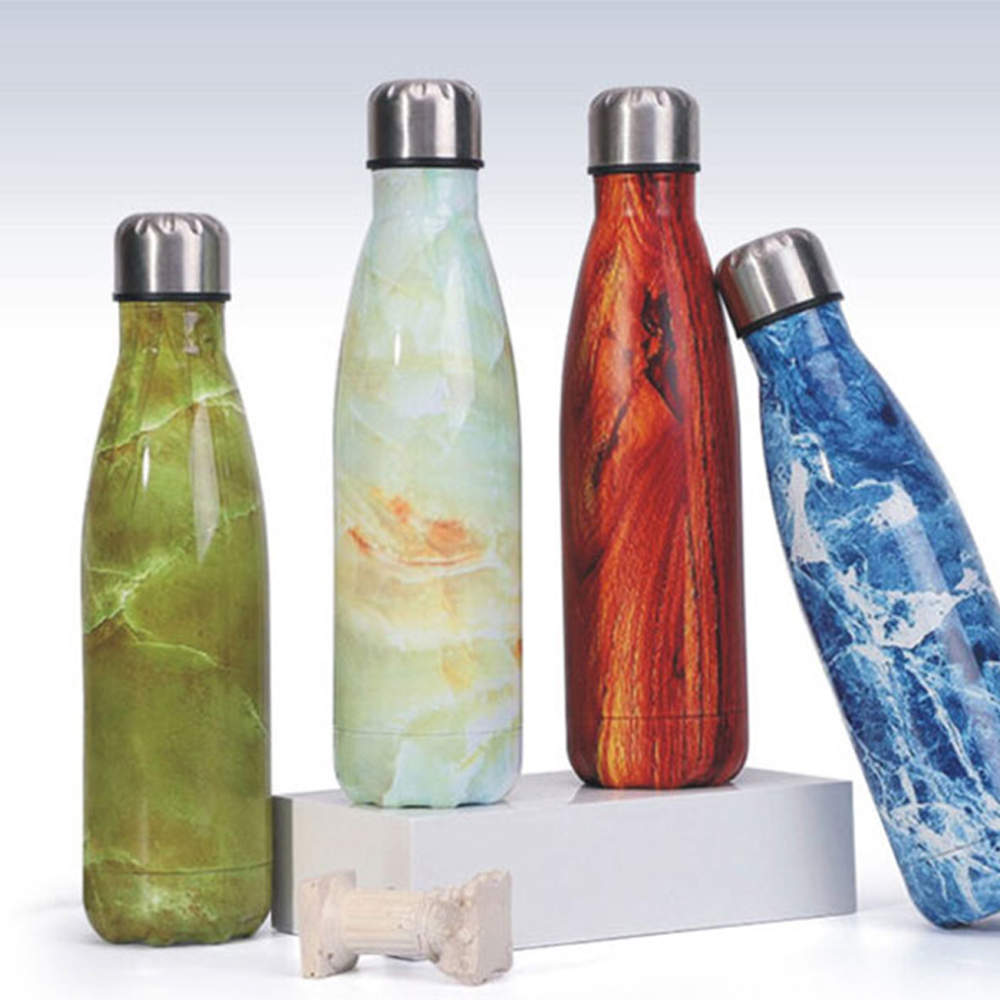
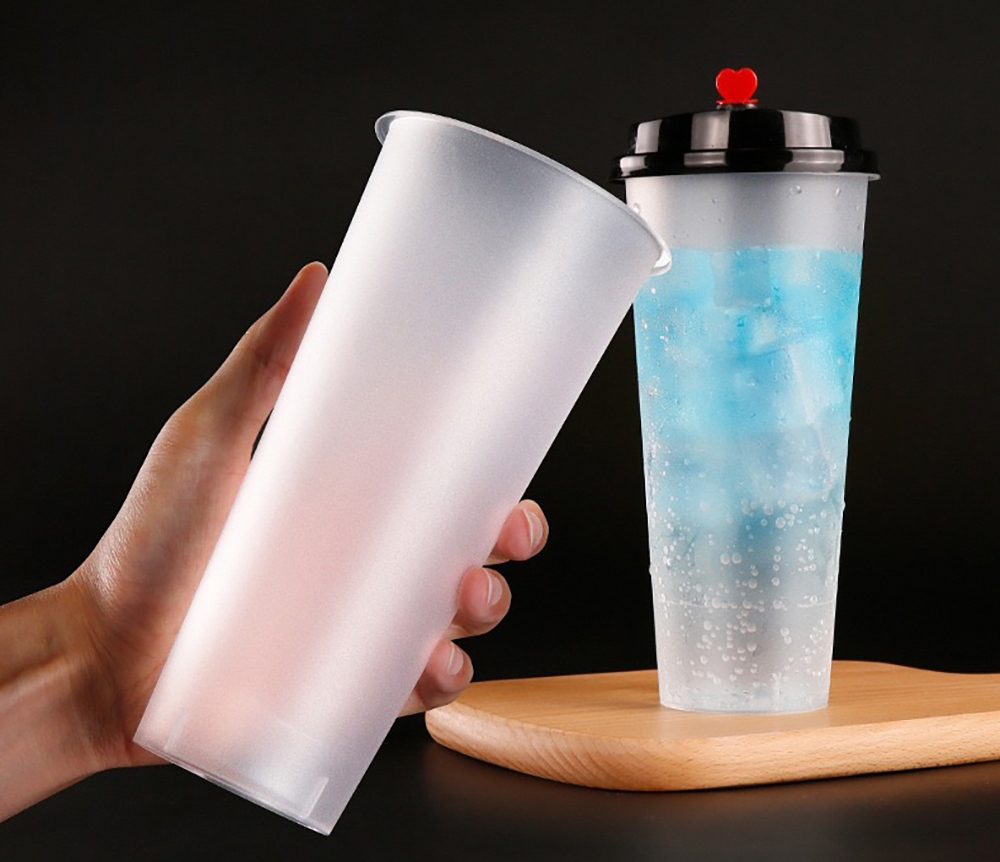
Gelas minuman buram semakin populer karena tampilannya yang stylish dan matte, cengkeramannya yang lebih baik, dan daya tahannya yang praktis. Lapisan buram yang lembut selaras dengan "estetika influencer" modern, membuat minuman terlihat lebih premium dan menarik secara visual. Permukaan bertekstur juga menawarkan penanganan yang lebih baik, mengurangi sidik jari dan goresan, serta meningkatkan pengalaman pengguna. Bagi produsen, masterbatch buram mudah digunakan, sangat kompatibel dengan material PP dan PET, dan membantu menurunkan biaya produksi dengan menghilangkan perawatan permukaan tambahan. Masterbatch ini juga sepenuhnya dapat didaur ulang, mendukung kemasan yang lebih berkelanjutan. Masterbatch buram menciptakan efek matte yang seragam dan berkualitas tinggi dengan difusi cahaya yang sangat baik, menjadikannya ideal untuk memproduksi gelas buram dan produk plastik transparan lainnya.