
- +8615880211820
- [email protected]
- Tongan Industry Park, Xiamen
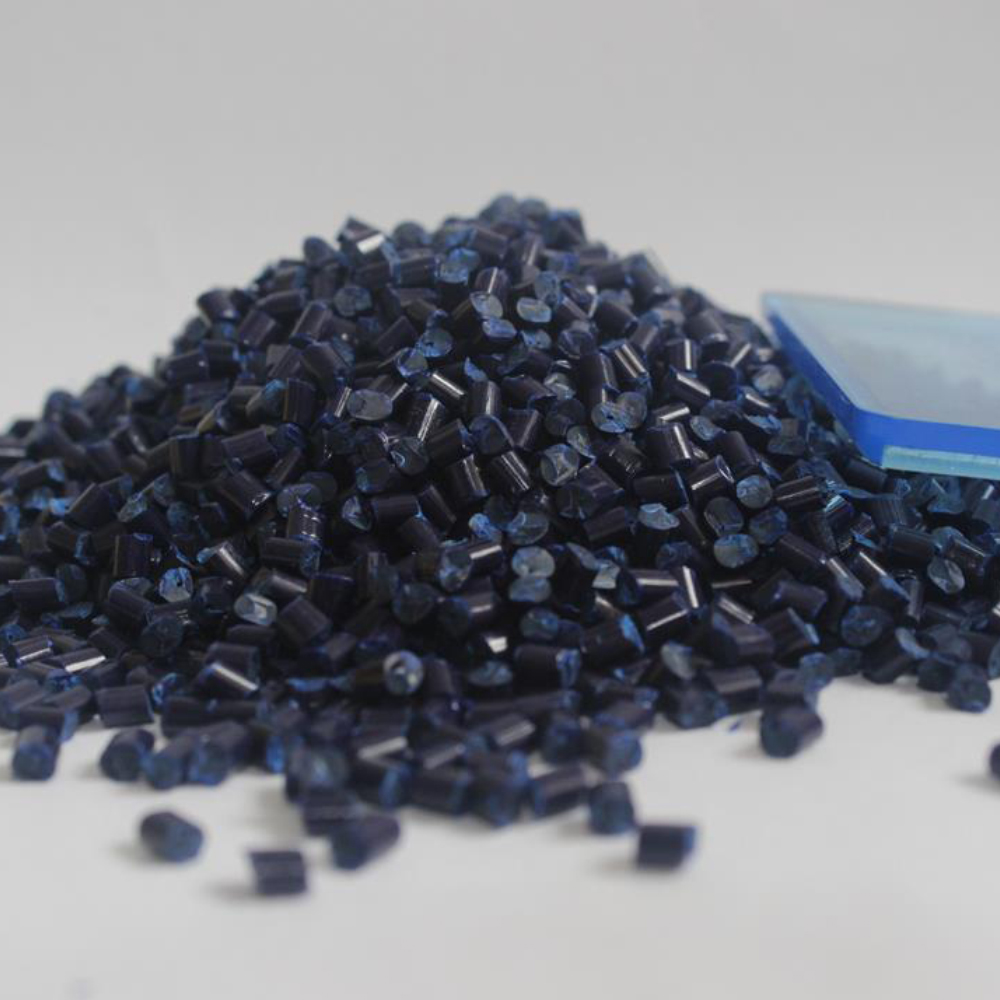
Plastic additives play a crucial role in optimizing the performance and quality of plastic products. One such essential additive is Antiblock Masterbatch, designed to address issues related to blocking and improve overall efficiency in plastic manufacturing. This article explores the features and benefits of Antiblock Masterbatch, as well as its counterpart, Slip Masterbatch, in enhancing the properties of plastic products.
Antiblock Masterbatch: Addressing Blocking Issues Blocking is a common challenge in plastic film manufacturing, occurring when two layers stick together during processes like extrusion, conversion, or storage. Traditional inorganic antiblocks, such as those based on siliceous minerals like diatomaceous earth and talc, have been widely used to mitigate this problem. However, Tosaf offers a range of advanced Antiblock Masterbatches that go beyond traditional solutions.
Preventing Unwanted Air Bubbles: Antiblock Masterbatch effectively addresses the formation of unwanted air bubbles during the manufacturing process, preventing small localized flaws that can grow over time.
Minimizing Blocking Effect: The masterbatch reduces the adhesion between two smooth layers of film, preventing the blocking effect in plastic sheets. This enhancement significantly improves product durability and standards.
Polymer Compatibility: Antiblock Masterbatch is suitable for polymers like polyolefins and polyesters, which inherently face blocking issues. It acts by producing a slight roughening of the surface, facilitating easy opening of bags and quick separation of plastic sheets.
Slip Masterbatch: Improving Film Handling and Converting In addition to Antiblock Masterbatch, Slip Masterbatch is another valuable additive that aids in minimizing film-to-film contact during handling and converting processes. It provides the necessary slip properties to enhance film manageability.
Benefits of Slip Masterbatch:
Reduced Film-to-Film Contact: Slip Masterbatch minimizes film-to-film contact, making the handling and converting of film more efficient. This is particularly important in applications like take-up rolls and stacking finished converted films.
Versatile Applications: Slip Masterbatch finds applications across various industries, upgrading the quality and efficiency of plastic products by preventing sheets from sticking together.
Antiblock and Slip Masterbatches offer technical advantages such as preventing agglomeration of additives, dispersion problems, and improved shelf life due to the absence of solvents. The recommended dosage of masterbatch in relation to the raw material ranges from 1% to 5%.
The carrier of masterbatches must be identical or compatible with the polymer. For example, EVA or LDPE serves as a compatible carrier for polyolefins and nylon. Incompatibility may lead to changes in material properties.
Occasional adverse effects, such as the separation of masterbatch from the raw material, may occur. However, these can be mitigated through proper handling and the use of peristaltic pumps. Masterbatches are compatible with various processes, except for rotational molding, plastisol, and other liquid resin systems.
Conclusion: Antiblock and Slip Masterbatches are indispensable additives in the plastic industry, offering tailored solutions to common challenges. By addressing blocking and minimizing film-to-film contact, these masterbatches contribute to the production of high-quality plastic products with improved durability and processing efficiency. Choosing the right masterbatch based on film properties, applications, and polymer compatibility is crucial for achieving optimal results in diverse plastic manufacturing processes.
Our masterbatches find a multitude of applications across diverse industries. Whether in plastics, textiles, or various manufacturing processes, our masterbatches play a pivotal role in enhancing product quality and performance. With customizable formulations, they offer color consistency, UV protection, flame resistance, and more, making them the go-to solution for countless applications. From automotive parts to packaging materials, our masterbatches are the trusted choice for achieving superior results across a wide spectrum of industries.
Our custom masterbatches are designed to match specific polymers, ensuring optimal performance when incorporated into your selected material. We have the capability to produce masterbatches suitable for a variety of polymers mentioned below, and many more. If you’re working with a material that isn’t listed here, please don’t hesitate to reach out to our knowledgeable technical team to explore the possibility of meeting your specific needs.

Low Density Polyethylene – Somewhat more translucent than HDPE and considerably more pliable, primarily employed in flexible packaging, tote bags, pliable tubing, film applications, and similar uses. Like HDPE, it has limited transparency characteristics. It exhibits outstanding chemical resistance to alcohols, acids, and alkalis but has restricted resistance to hydrocarbon solvents and mineral oils. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can initiate degradation.
High-Density Polyethylene – Featuring a somewhat milky-white appearance, this material finds wide application in rigid bottle packaging, injection-molded caps and closures, crates, and more. Its natural opacity can limit the degree of transparency attainable. HDPE exhibits superior chemical and solvent resistance when compared to LDPE.


PPCO Random & PPHO – A polymer with moderate clarity, employed in the production of caps and closures. It is also utilized for crafting household items, buckets, toys, and storage containers. Polypropylene offers flexibility without significant limitations on color or special effects. Random copolymer boasts greater clarity compared to homopolymer and is better suited for creating translucent shades.
PPCO Block – Similar to PPCO but enhanced for increased impact resistance. An additive renders the polymer white, resulting in high opacity. This characteristic may limit the achievable transparency.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) – Polyester materials exhibit robust mechanical strength along with excellent chemical resistance and barrier properties. PET is frequently chosen for the production of carbonated beverage containers. Moreover, polyester can be spun and employed in textile manufacturing for clothing. PET is highly transparent, making it an excellent choice for translucent packaging, although a subtle hint of “yellowing” may impact extremely light tints.


Polybutylene Terephthalate – A crystalline thermoplastic engineering polymer frequently employed as an insulating material within the electronics sector. This substance belongs to the polyester category, showcasing a remarkable equilibrium of attributes and processing qualities.
General Purpose Polystyrene – Exhibiting a glass-clear appearance but possessing minimal impact resistance, this material finds its primary application in CD cases. Its notable clarity renders it suitable for creating translucent hues, although an occasional violet tint may be discernible.


High Impact Polystyrene – Derived from GPPS by incorporating an impact-enhancing agent to boost its resistance to impacts. This added component results in the polymer becoming white, and different formulations provide varying degrees of opacity. Typically employed in the fabrication of game pieces, toys, and similar items. Its pronounced whiteness can pose challenges when aiming for translucent coloration. Specialized alternatives like K-Resin and Styrolux are accessible in the market to attain the same level of translucency as GPPS.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) – A more robust iteration of High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) employed in high-value components. ABS exhibits greater durability compared to HIPS-made components, although it encounters similar challenges when attempting to achieve translucent colorations. Just like HIPS, ABS offers specialized translucent variants. Owing to its durability, ABS is commonly used in crafting casings for power tools.

Polyamide (6, 66) – Nylon represents a versatile grade extensively employed in mechanical construction and maintenance. Its popularity stems from its excellent blend of mechanical strength, rigidity, mechanical damping characteristics, and effective electrical insulation capabilities. Consequently, nylon is a preferred material for manufacturing electrical enclosures. PA66 serves as a common alternative to metal across diverse applications, with its chemical and physical attributes closely resembling those of PA6. PA6 exhibits superior impact resistance and resistance to solvents, albeit with a heightened susceptibility to moisture absorption.
Styrene Acrylonitrile Copolymer – Possessing transparency and outstanding chemical and heat resistance, SAN also boasts good rigidity, tensile strength, and flexural strength. Thanks to its high-gloss finish, SAN is commonly chosen for cosmetic packaging purposes. However, achieving light tint colors with SAN can be challenging due to the violet dyestuffs inherent in the material, which are utilized to enhance its visual appearance during manufacturing.


Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol – PET with the incorporation of glycol. This glycol addition enhances flow properties but diminishes strength. PETG can be extruded to create bottles and can be formed into sheets for producing ‘blister’ style packaging.
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) or Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) – TPU finds diverse uses in applications such as automotive instrument panels, caster wheels, power tools, medical devices, as well as various extruded film, sheet, and profile applications. TPEs are employed across a wide range of applications in industries spanning automotive, medical, construction, electrical, appliances, packaging, and industrial sectors.
Frequently asked questions about our masterbatch




©2023. Masterbatch Manufacturer All Rights Reserved.
Our team will send back the best offer in 20 minutes.